| Note |
|---|
Warning: You’re entering an advanced section for engineers and developers. Topics described below are not a needed for most PackOS users. They require some programming skills, but can help you better tune PackOS to your needs |
Introduction
You can think of the pre-processing functions as tools that you can use to perform computations on signals that PackOS receive before they are processed and assigned to specific machines.
Example use cases include:
hex-to-decimal conversion
bit selection
value multiplication
signal aggregation
line flow change
changeover end
Syntax
Each function is a C# script. It’s a strongly typed language requiring you to handle type conversions, but also making sure there are no syntactic errors by compiling the script before persisting.
Head to https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/csharp/tour-of-csharp/tutorials/ for a tutorial
In addition to variables and services provided by the platform (more about that below), all operations on Double, Int, String or DateTime variables are available to you.
Configuration
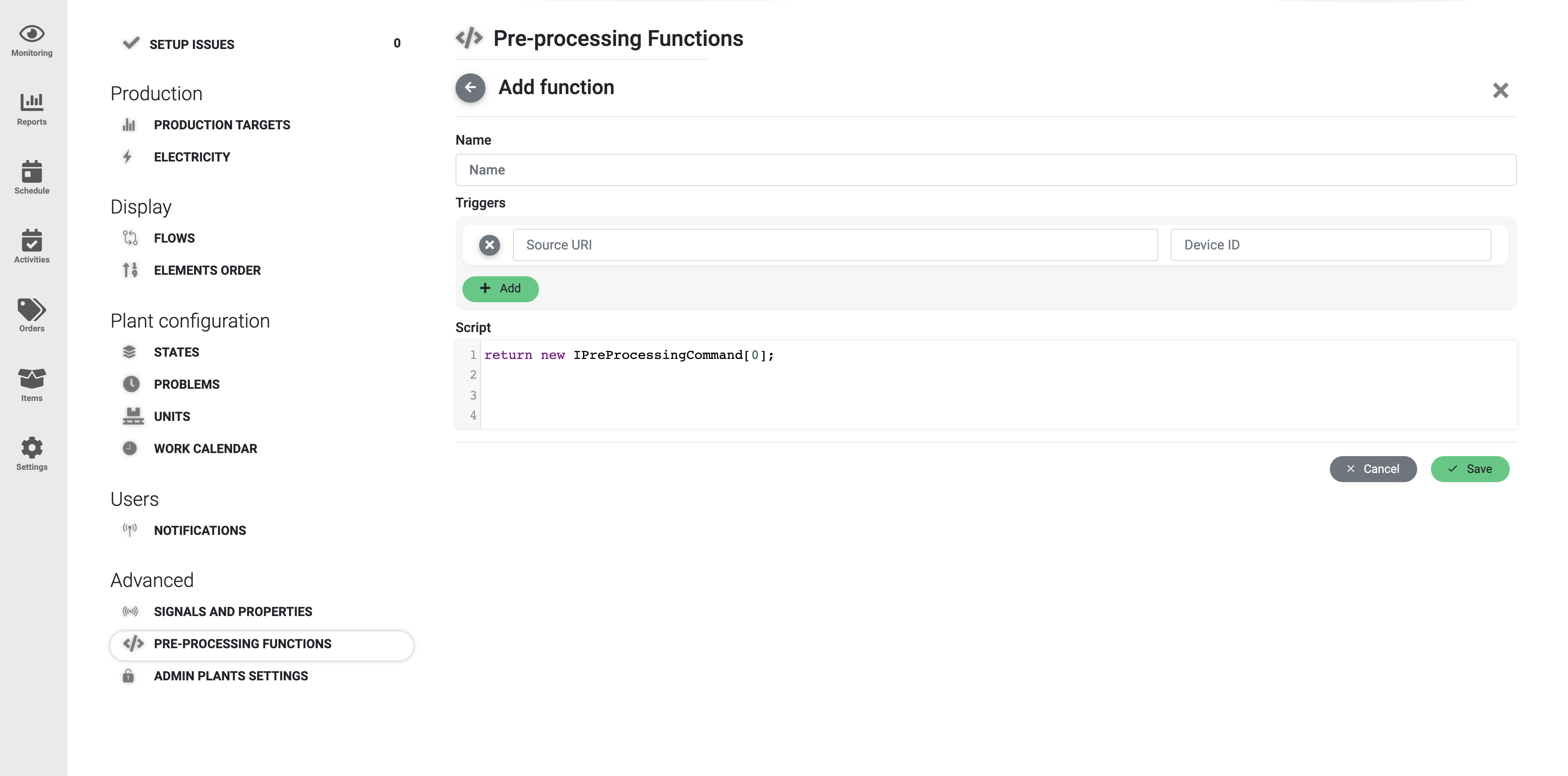
In order to configure pre-processing functions in PackOS, you will need to:
1. Go to Settings by clicking on the Settings button in the left sidebar.
2.Click on the Pre-Processing Functions in the section Advanced located at the bottom of the page.
Specifying trigger tags
Each function is triggered when one of the defined tags is observed. Each tag is a pair of Source URI and Device ID.
Source URI usually specifies OPC UA tag available in the OPC Server. If another type of data source is used – it’s the corresponding tag assigned to that node in LogiX Gate.
Device ID further specifies which data source (LogiX Gate’s input) for the Source URI is used, mostly needed when there are multiple OPC Servers publishing the same tags.
| Info |
|---|
In the future, you’ll be able to set a time trigger on the function |
Available variables
The following variables are available and can be used in the script. There are nested objects containing multiple simple types, and services which can be used to query more data.
TriggerValue [string?]-- value from the message which triggered the functionTrigger [object]– details about the triggerNodeId [string?]-- Source URI from the message which triggered the functionApplicationUri [string?]-- Device ID from the message which triggered the functionValue [object]-- details about the trigger valueValue [string?]-- same as TriggerValue variable aboveSourceTimestamp [DateTime]-- timestamp of the messageStatusCode [object?]-- details of the connection errorSymbol [string]-- Name of the issueCode [long]– OPC error code
TagValue [service]-- access to current values of all received tagsstring GetValue(string sourceUri, string? deviceId)– getting raw string value of a tag (it does not necessarily need to be one of the trigger tags)T? GetValue<T>(string sourceUri, string? deviceId)– value of a tag converted to the desired type (or a default value of that type if conversion invalid)DateTime? GetUpdate(string sourceUri, string? deviceId)– timestamp of the last update of this tag
Element [service]-- access to current element stateWorkLog? WorkLog(string elementName)– current state of the elementIsForced [bool]-- true/false if the current state is forcedWorkStateName [string]-- code name of the current state (e.g. holdup)StartDate [DateTime]-- timestamp when the state bugRootStateName [string?]-- code name of the root state (e.g. holdup)RootStartDate [DateTime?]– timestamp of the root state
Store [service]-- memory space for custom variablesbool TryGet(string key, out string value)– getting value of the keyvoid Set(string key, string value)– setting value of the key
In service methods, specifying deviceId is optional. If not provided, the first matching Source URI value will be returned.elementName is either directly a name of the line, or a path to a machine in the format:
LineName/ MachineName (e.g. Line1/Filler)
Function result
Pre-processing function returns a list of commands, all implementing IPreProcessingCommand type.There are numerous command types available, each function can return a mix of them. New commands will be added in the future to cover more scenarios.
Tag(string value, string sourceUri, string? deviceId = "")- returns a new value with new SourceUri and DeviceId which then can be mapped to one of the signals in machine or line definition.SetFlow(string lineName, string flowName)- changes active flow on the selected lineEndForcedState(string elementName)- forces state recalculation from rules on the provided element, ending the forced stateResetBuffers(string lineName)- resets all tracked line buffers (see: [In Progress: Differential waste calculation])
Example functions:
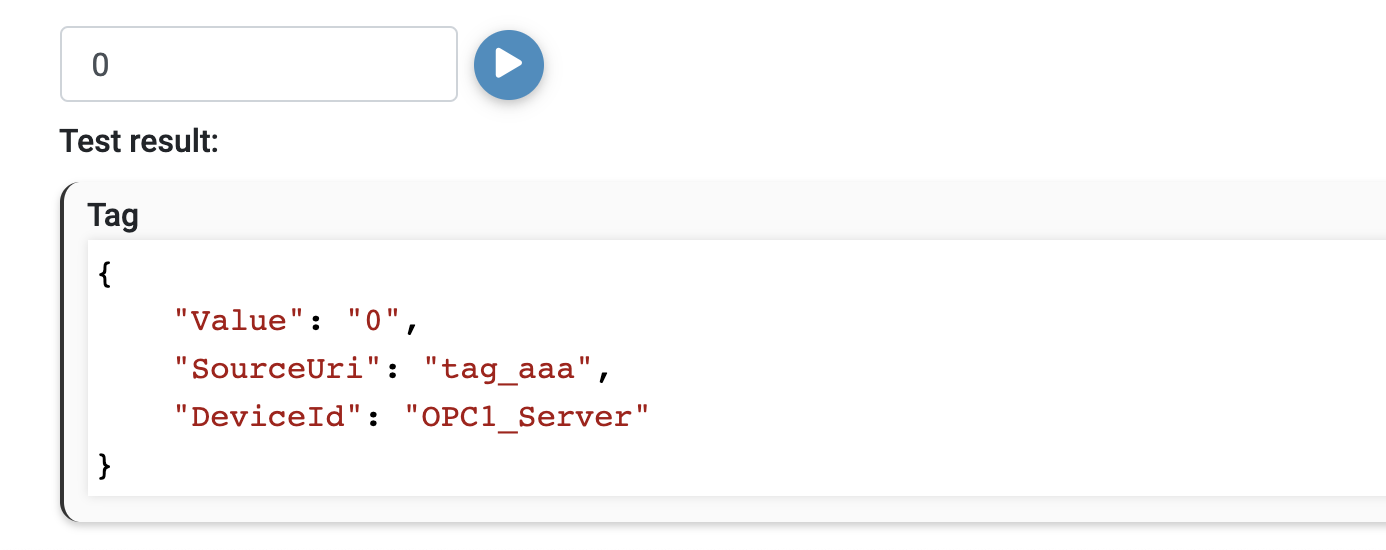
The simplest valid function can return just an empty list:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
return new IPreProcessingCommand[0]; |
2. Calculate a sum of 3 tags “a”, “b”, “c” and return it as tag “sum”
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
// 1. Use tag dictionary to get latest values for each of the tags
double a = TagValue.GetValue<double>(“a”);
double b = TagValue.GetValue<double>(“b”);
double c = TagValue.GetValue<double>(“c”);
// 2. Calculate the sum
double sum = a + b + c;
// 3. Return the calculated variable as a command
return new []
{
new Tag(sum, “sum”)
}; |